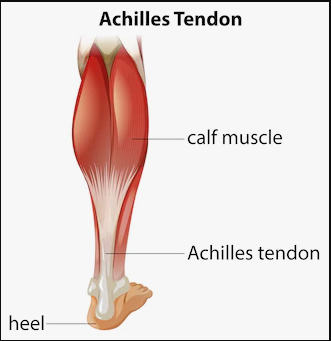
Achilles tendonitis is a common condition that affects the Achilles tendon, the largest and strongest tendon in the human body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and plays a crucial role in the movement, allowing us to walk, run, jump, and perform other activities that require ankle and foot movement. However, this tendon can become inflamed and painful due to overuse, sudden changes in activity, or improper stretching and warm-up techniques. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, and prevention strategies for Achilles tendonitis.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis
The most common symptom of Achilles tendonitis is a pain in the heel and ankle area, particularly when walking, running, or climbing stairs. Other symptoms may include stiffness, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area. In some cases, the pain may be felt only during or after physical activity, while in others, it may be present throughout the day.
Causes and Risk Factors of Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is caused by repetitive or excessive stress on the tendon, leading to small tears and inflammation. Some common activities that can cause this condition include running, jumping, playing sports, and climbing stairs. However, it is not only athletes that are at risk of developing this condition, as even those who are less active may also develop Achilles tendonitis.
- Age: As we age, our tendons naturally become less flexible and more prone to injury.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop Achilles tendonitis than women.
- Foot structure: Individuals with flat feet or high arches may be at a higher risk for Achilles tendonitis.
- Tight calf muscles: Tight calf muscles can put extra stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Previous injury: A previous injury to the ankle or foot can increase the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis.
Prevention and Management of Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis can be managed by taking rest, applying ice to the affected area, and taking over-the-counter pain medication to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy exercises, such as stretching and strengthening the calf muscles, can also help to improve flexibility and reduce stress on the tendon. In more severe cases, a doctor may prescribe a brace or splint to immobilize the ankle and allow the tendon to heal. In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a ruptured Achilles tendon.
To prevent Achilles tendonitis, it is important to properly stretch and warm up before engaging in physical activity. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of activity can also help to prevent overuse injuries. Wearing proper shoes with adequate support can also help to reduce stress on the Achilles tendon. In addition, regular exercises that aim to strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility can also reduce the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis.
Conclusion
Achilles tendonitis is a common condition that can cause pain and inflammation in the heel and ankle area. It is caused by repetitive or excessive stress on the tendon and can be prevented by properly stretching and warming up before physical activity, wearing proper shoes, and regular exercises that aim to strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility. If you are experiencing symptoms of Achilles tendonitis, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening.